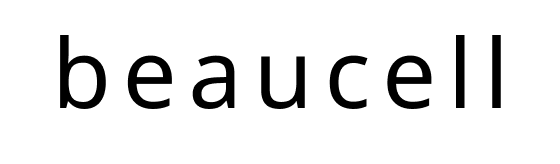Potential of stem cells called pluripotent cells
In recent years, stem cells (Stem Cells) have been the focus of much attention in regenerative medicine and anti-aging beauty. When people are born, they have approximately 300 million stem cells, but these cells decrease with age. The skin then loses its firmness and elasticity, and wrinkles, sagging, dark circles under the eyes, sagging eyes, and lines increase and the skin becomes thinner, resulting in aging. Stem cells are gaining attention in anti-aging treatments.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are the source of a wide variety of cells. Skin, muscles, bones, blood, and all tissues and organs are all made of cells. And each cell has a life span; it dies and new cells are born with the power of stem cells. Hair and nails grow, wounds and broken bones heal, and skin is renewed. Stem cells are capable of producing new cells. Stem cells have two major functions. One is the ability to produce various cells in our body, such as skin, red blood cells, nerves, and muscles (differentiation ability), and the other is the ability to divide into cells with the same ability as themselves (replication ability).
differentiation capacity
Ability to produce a variety of cells that make up the human body, such as blood vessels, nerves, and muscles blood vessels, nerves, muscles, etc., that make up the human body.
reproductive capability
The ability to create an alter ego with the same abilities as oneself.Stem cells can also increase the number of stem cells themselves.
Stem cells are also called pluripotent cells because they have the ability to re-generate and replenish new cells to maintain tissues and organs that are constantly being replaced, and to replenish cells lost due to tissue damage.
Stem cells are taken from outside the body through an infusion.
Stem cells are innate in the body of all living organisms, not just us humans, but they diminish with age. However, recent advances in medical technology have made it possible to take in cultured stem cells from outside the body through intravenous infusion. In Malaysia, a country with advanced stem cell technology, it is allowed to use stem cells from other people through intravenous infusion. For example, stem cells from a 0-year-old child taken from the umbilical cord (umbilical cord) are cultured and taken into the body via intravenous infusion, causing improvement in physical strength and self-healing power, and thus rejuvenating effect can be expected. Stem cell infusion is also called "the ultimate anti-aging" because it is expected to rejuvenate the body at the cellular level.

Stem cell serum
Recently, “stem cell serums” have become popular, but in the case of cosmetics, they only contain nutrients (growth factors) to energize the body’s own stem cells, not the stem cells themselves, and are effective only for day care.
Intravenous infusion of stem cell culture supernatant solution
The supernatant fluid generated when stem cells are cultured contains many nutrients (growth factors) to activate stem cells, and infusion of this fluid is also popular. However, it does not contain the stem cells themselves.
Image of usage
Rejuvenation at the cellular level: Stem cell infusion brings healthy stem cells into the body
Daily care: Utilize stem cell serum, IV infusion of stem cell culture supernatant solution, etc…
Various benefits that can be expected from stem cell infusion

Disease
– Decreases risk of diseases such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease
– Decreases serum concentrations of cholesterol and triglycerides.
– Reduce allergies.
– Relieves symptoms of menopause and premenopause.
– Accelerates wound healing and reduces the size of damaged cells.

Body
– Increases metabolism and physical fitness.
– Helps build muscle mass.
– Improve digestion and constipation
– Improves the movement of joints
– Promotes sexual desire and endurance.
– Promotes the growth of new blood vessels and improves intracellular blood flow.

Face
– Reduce wrinkles.
– Improve skin elasticity and thickness.
– Brighten complexion and improve skin tone.
– Remove open pores and dark circles under the eyes.
How do stem cells work after injection?
When young, active stem cells in the early stages of development are injected, they circulate through the body until they find the target cells from the injection site.

Automatic detection of inflammatory foci
Regulates immune response
Cellular tissue repair and regeneration

Regulates vascular expansion

Prevention of immature cell death

Reduced scarring
Stem cells stimulate cells and tissues to function efficiently again by marking old, inactive, and deteriorated cells and secreting growth and repair factors. Therefore, it is said that it is easy to experience functional recovery, especially in weak areas, when stem cell infusion is performed.
Stem cells can also, under the right conditions, stimulate dormant cells and restore the body’s natural resilience. By incorporating young, fresh stem cells, the tissues and organs themselves can also retain their vitality and life force.
Types of stem cells
Humans, Animals, Plants
Not only humans, but animals and plants also have stem cells.
Recently, cosmetics derived from animal and plant stem cells have appeared, but it is said that “human stem cells for humans” are the most effective.
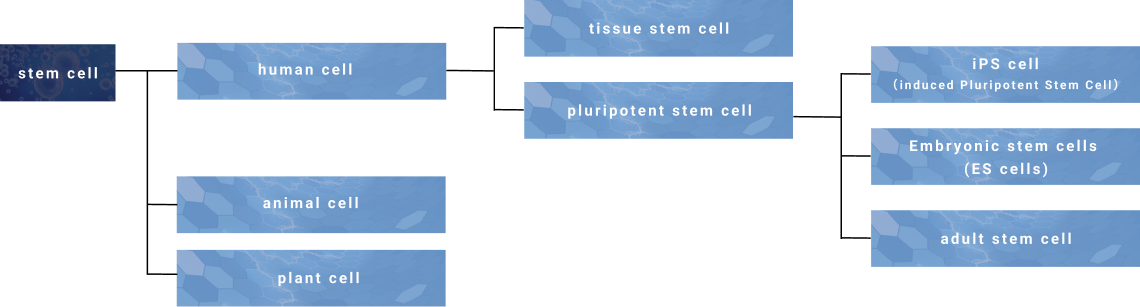
Tissue stem cells and pluripotent stem cells
Tissue stem cells are stem cells that replenish missing cells in a given tissue or organ, such as skin or blood.
Tissue stem cells cannot become any kind of cell, but can only differentiate into cells of the blood system if they are hematopoietic stem cells that produce blood, or into cells of the nervous system if they are neural stem cells that produce the nervous system, and so on.
Pluripotent stem cells, on the other hand, are cells that can also produce various tissue stem cells. Incidentally, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), for which Professor Yamanaka of Kyoto University won the Nobel Prize, are artificially created “pluripotent stem cells” based on ordinary cells. Pluripotent stem cells include embryonic stem cells (ES cells) and iPS cells derived from fertilized eggs, and adult stem cells that actually function in various tissues and organs.
Classification by Tissues and Organs
Among adult stem cells, the properties of stem cells vary from tissue to tissue and organ to organ.
MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells), which have high replication and differentiation potential, are often used for infusion, as are adipose stem cells, dental pulp stem cells, bone marrow stem cells, umbilical cord stem cells, and cord blood stem cells.
*Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a classification of adult stem cells. Mesenchymal stem cells have a very high ability to divide and proliferate (replicative capacity) and have the ability to “differentiate” into nerve, muscle, fat, bone, etc., in addition to cells of one lineage.
State-of-the-art stem cell infusion in Malaysia
Malaysia, known as an honor student in Southeast Asia, is actually an advanced medical country, especially in practical applications related to stem cells. In Malaysia, laws and regulations regarding stem cell therapy are in place, and it is possible to receive high-quality stem cell infusion with peace of mind.
For example, in Japan, laws and regulations regarding stem cell therapy lag behind, and there are considerable restrictions, such as not being able to receive infusions of stem cells cultured from other people’s cells. In Malaysia, on the other hand, a wide range of procedures are allowed under strict standards. Furthermore, in Malaysia, there are many companies that culture stem cells, and the cost of culturing stem cells is relatively low despite their high quality.